CHAPTER 3: LEGAL STRUCTURE OF MUTUAL FUNDS IN INDIA
Mutual fund is a vehicle (in the form of a “trust”) to mobilize money from investors, to invest in different markets and securities, in line with stated investment objectives. Through investment in a mutual fund, an investor can get access to equities, bonds, money market instruments and/or other securities, that may otherwise be unavailable to them and avail of the professional fund management services offered by an asset management company.
SEBI has stipulated the legal structure under which mutual funds in India need to be constituted. The Structure is as follows:

> MFs are constituted as Trusts under the Indian Trusts Act, 1882. MF trust is created by one or more Sponsors
> Every trust has beneficiaries who are the investors who invest in various schemes of the mutual fund.
> Operations of the MF trust are governed by a Trust Deed, which is executed between the sponsors and the trustees.
> Day to day management of the schemes is handled by an Asset Management Company (AMC) appointed by the sponsor or the Trustees.
> The record of investors and their unit- holding may be maintained by the AMC itself, or it can appoint a RTA.
Key Constituents of a Mutual Fund
- Sponsors
- Board of Trustees
- Custodians
- Assets Management Company
- mutual Fund Trust
Sponsors-
- The application to SEBI for registration of a mutual fund is made by the sponsor(s).
- The sponsor should have a soundtrack record and reputation of fairness and integrity in all business transactions.
- The sponsor should be a fit and proper person for.
- Association of Mutual Funds in India’s (AMFI) website lists the names of all the Asset Management Companies, which are members of AMFI, in terms of the category of the sponsor, viz., Banks, Institutions, Private sector, etc.
Board of Trustees-
- Trustees ensure mutual fund complies with all the regulations and protects the interests of the unit-holders.
- The sponsor will have to appoint at least 4 trustees. If a trustee company has been appointed, then that company would need to have at least 4 directors on the Board.
- Further, at least 2/3rd of the trustees on the Board of the trustee company would need to be independent trustees i.e., not associated with the sponsor in any way.
- Prior approval of SEBI needs to be taken before a person is appointed as Trustee.
- SEBI regulations prescribe eligibility criteria of trustee.
Assets Management Company-
- The AMC is responsible for conducting the activities of the mutual fund.
- A minimum net worth of Rs. 50 crores maintained on a continuous basis.
- It arranges for the requisite offices and infrastructure, engages employees, provides software, handles advertising and sales promotion, and interacts with regulators and various service providers.
- AMC ensure that the investment of funds pertaining to any scheme is not contrary to the provisions of the SEBI regulations and the trust deed.
- The appointment of an AMC can be terminated by a majority of the trustees, or by 75% of the Unit- holders.
Custodians-
- The custodian has custody of the assets of the fund. As part of this role, the custodian needs to accept and give delivery of securities for the purchase and sale transactions of the various schemes of the fund. Thus, the custodian settles all the transactions on behalf of the mutual fund schemes.
- All custodians need to register with SEBI under the SEBI (Custodian) Regulations 1996. The Custodian is appointed by the trustees.
- A custodial agreement is entered into between the trustees and the custodian.
- The custodian also tracks corporate actions such as dividends, bonuses and rights in Companies where the fund has invested.
Organization Structure of Asset Management Company
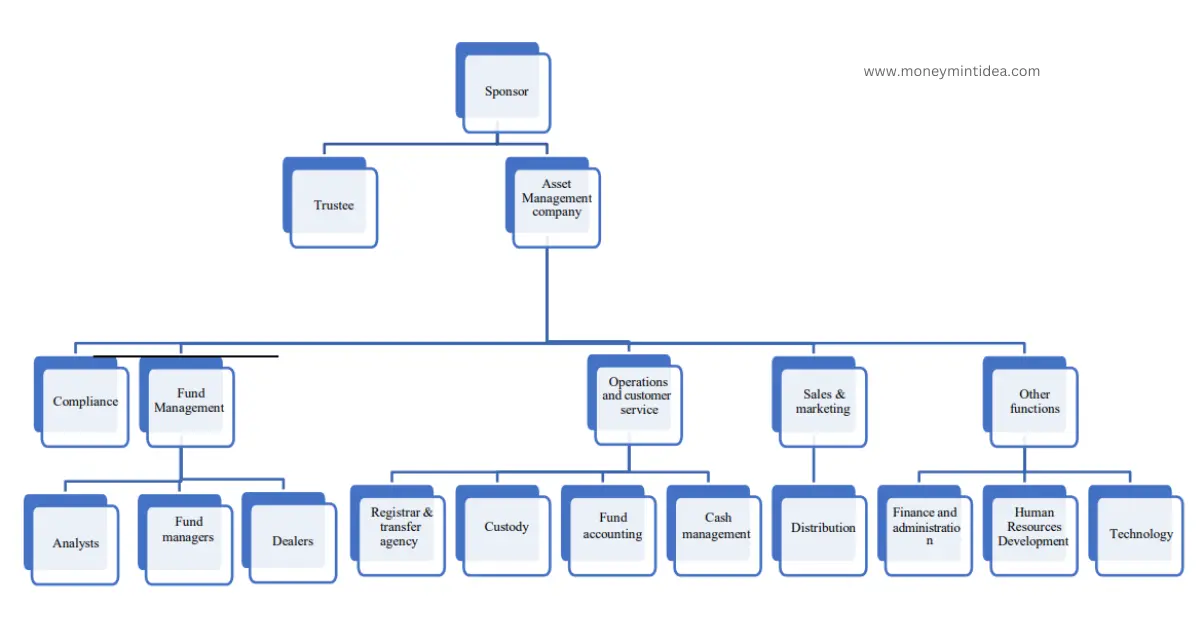
The various functions within an AMC are:
- Compliance: Compliance Officer needs to ensure all the legal compliances. In the scheme documents of new issues, the Compliance Officer signs a due-diligence certificate to the effect that all regulations have been complied with, and that all the intermediaries have the statutory registrations and approvals.
- Fund Management: This team is to invest the investors’ money in line with the stated objective of the scheme and to manage the same effectively. The team can be generally broken into three sub- teams, viz., the analysts, the fund managers, and the dealers.
- Sales and Marketing Team: This team reaches out to the investors through mass media, marketing campaigns and through a distribution channel.
- Operations & Customer Service Team: When a customer visits a branch office of an AMC, he is attended to by the customer services team known as front office team. There is also a team in the back office to help investors by resolving various queries. Many AMCs have adopted information technology solutions and have set up call centers and chat bots to answer customer queries and resolve service issues.
Other Functions:
- The Accounts team handles the finances of the AMC.
- Administration Department looks after various facilities, offices, and other infrastructure.
- HR department is responsible for attracting and retaining talent within the firm.
- Information Technology department takes care of the IT infrastructure required by various functions and departments, AMC website, as well as many facilities offered to investors and distributors with the help of technology.
Role and Support function of Service Providers
1. Fund Accountants: performs the role of calculating the NAV, by collecting information about the assets and liabilities of each scheme. The AMC can either handle this activity in-house or engage a service provider.
2. Registrar and Transfer Agents: The RTAS maintain investor records. Their offices in various centers serve as Investor Service Centers (ISCs), which perform a role in handling the documentation of investors. The appointment of RTA, though not compulsory, is done by the AMC. The AMC can choose to handle this activity in- house. All RTAs need to register with SEBI.
3. Auditors: Accounts of the mutual fund schemes need to be maintained independently of the accounts of the AMC. The auditor appointed to audit the mutual fund scheme accounts needs to be different from the auditor of the AMC. While the scheme auditor.
4. Collecting Bankers: The investors’ money goes into the bank account of the scheme they have invested in. These bank accounts are maintained with collection bankers who are appointed by the AMC.
5. KYC Registration Agencies: KRAs process various details and documents to establish the identity of the investor and assign a number through a letter. A copy of this letter can be submitted to any SEBI registered intermediary with whom the investor wants to transact.
6. Valuation agencies: Fair valuation of debt securities that are non-traded or thinly traded. According to these guidelines, there have to be at least two valuation agencies that provide valuation matrix.
7. Distributors: Distributors have a key role in selling suitable types of MF Schemes to their clients/investors. A distributor can be empaneled with more than one AMCs. Distributors can be individuals or institutions such as distribution companies, broking companies and banks.
8. Credit Rating Agencies: Credit rating agencies rate debt securities issued by various issuers. Certain categories of debt funds such as corporate bond funds, credit risk funds are defined on the basis of credit rating.
9. Stock exchanges and the transaction platforms: Investors can now transact in mutual fund units through the SEs. While units of close-ended funds and ETFs are compulsorily listed on at least one SE, units of open- ended funds are also available through special segments on the SE. At BSE, this segment is known as BSE-Star MF; while at the NSE, it is called NSE Mutual Fund II Platform (NMF-II).
Role and Function of AMFI
1. Association of Mutual Funds in India (AMFI) is the association of all the registered Asset Management Companies.
2. Objectives of AMFI is to define and maintain high professional and ethical standards in all areas of operation of the mutual fund Industry.
3. Functions are:
- To interact with SEBI and to represent to SEBI on all matters concerning the mutual fund industry.
- To represent to the Government, RBI and other bodies on all matters relating to the mutual fund Industry.
- To undertake a nationwide investor awareness programme to promote proper understanding of the concept and working of mutual funds.
- To protect the interest of investors/unitholders.
- To regulate the conduct of distributors including disciplinary actions (cancellation of ARN) for violations of Code of Conduct.
4. Major role of AMFI involves the registration of mutual fund distributors, by allotting them AMFI Registration Number (ARN).
CHAPTER 1: Investment Landscape
CHAPTER 2 : Concept And Role Of A Mutual Fund
Chapter 3: Legal Structure Of Mutual Funds In India
Chapter 4: Legal And Regulatory Framework
Chapter 5: Scheme Related Information
Chapter 6: Fund Distribution & Channel Management Practices
Chapter 7: Net Asset Value, Total Expense Ratio & Pricing Of Units
Chapter 10 : Risk, Return And Performance Of Funds
Chapter 11 : Mutual Fund Scheme Performance
Chapter 12 : Mutual Fund Scheme Selection































